
FIPS 140-2
FIPS 140-2 (Federal Information Processing Standard Publication 140-2) is a U.S. government standard that specifies the security requirements for cryptographic modules used to protect sensitive data. It ensures that cryptographic solutions meet strict guidelines for secure operation in government and regulated environments.

Sanitize
Sanitize features provide standardized, secure, and verifiable methods to irreversibly erase all user data stored on SSDs, including areas that are not accessible through regular deletion or formatting.

Anti-Sulfuration
Sulfur corrosion has become an increasingly critical concern in environments with high levels of atmospheric pollution and relative humidity. These conditions accelerate the degradation of electronic components, primarily due to the formation of silver sulfide. This corrosive byproduct forms when silver reacts with airborne sulfur, significantly increasing electrical resistance and potentially leading to open circuits in components such as chip resistors.

DataGuard
The SP Industrial DataGuard specific device is equipped with a hardware switch that enables WriteProtect and QuickErase. The DataGuard feature is activated when a specific connector is placed on the designated pin header, either during the initial power-up sequence or at any point during operation.

Debug Access Port (DAP)
Debug Access Port (DAP) is a debug transmission interface reserved through SSD design. When the system encounters an issue, the user can shut down the system first and connect to the DAP function.

FWxpress
SP FWxpress is a remote service solution designed to simplify SSD firmware updates, accelerate bug fixes, and significantly reduce system downtime.

FrameSolid
With the advancement of solid-state drive (SSD) technology, there is an increasing demand for long-term, stable write performance. While traditional SSDs provide high-speed read and write performance initially, their performance often degrades significantly over time, posing a major challenge for applications that require continuous, stable operation. FrameSolid technology was developed to address this issue by ensuring that SSDs maintain stable performance during prolonged use, making it particularly suitable for applications that demand reliable storage.

Advanced LDPC
Advanced Low-Density Parity-Check (LDPC) codes are sophisticated error-correction algorithms designed to enhance data reliability in high-performance storage and communication systems, such as SSDs and wireless networks. The core principle of LDPC involves using a matrix-based method to detect and correct errors, ensuring data integrity during transmission or storage.

Selected SSD Controller
SSD controller, also known as a processor, serves as the core logic that connects flash memory to the SSD’s input/output interfaces and executes firmware—often updatable—to support evolving features, while industrial SSDs not only deliver high-speed performance but also prioritize reliability, consistency, endurance, and manageability, making controller design especially critical in 24/7 industrial environments where multiple drives operate concurrently with minimal idle time and flash memory cells wear out due to sustained write workloads.
Conformal Coating
Conformal coating is a protective layer applied to printed circuit boards (PCBs) to shield them and their components from environmental damage and corrosion. Typically applied with a thickness of 30-210μm, the coating conforms closely to the shape of the PCB and its components, covering solder joints, exposed leads, traces, and other metalized areas. By enhancing resistance to moisture, pollution, dust, and chemical contaminants, conformal coating helps extend the lifespan of electronic products.

Underfill
Underfill technology is a cutting-edge solution designed to enhance the reliability of electronic components. The process involves injecting a specialized filling material between the bottom of components on a PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) and the substrate.
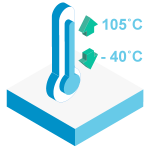
Wide Temperature
We are pioneers in developing high-performance products designed to endure extreme temperatures. Leveraging our Advanced Sorting technology, we have built a customized die bank database tailored for a variety of NAND chip brands and types. Our top-tier industrial solutions, including DRAM modules, operate reliably in temperatures as low as -40°C and as high as 105°C. These robust products are vital in critical sectors such as industrial processing, logistics, and telecommunications. To ensure their durability, we subject them to rigorous 3000 Power Cycle tests.

SMART IoT
S.M.A.R.T, short for Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology, is a monitoring system designed for early error detection in flash storage devices like solid-state drives (SSDs). SSDs use NAND flash memory, which stores data by moving electrons. However, repeated write cycles can gradually degrade the NAND chips, limiting the lifespan of the drive.

Thermal Throttling
Thermal throttling is a technology designed to dynamically regulate the operating frequency of devices, such as SSDs, to prevent overheating and maintain stable performance. This mechanism leverages real-time temperature monitoring through dual thermal sensors placed on both the PCB and the controller. Integrated with the SP SMART toolbox, these sensors continuously monitor the SSD's temperature to detect potential overheating.

End2End Protection
End-to-End (E2E) technology is a comprehensive approach to testing and monitoring systems from start to finish. Its primary goal is to simulate real user interactions and ensure the seamless operation of the entire system. By replicating user scenarios, E2E testing verifies whether various components and processes in the system work cohesively.

Advanced Power Shield
The Power Shield (PS) function activates when the external voltage drops to a critical level, such as from 3.3V to 2.7V. At this point, the voltage detection circuit inside the SSD controller triggers the power protection mechanism.

PFP+
Silicon Power implemented dual secure design for power failure protection+. All series of SP Industrial SSD with Power shielding firmware architecture protection when sensing unstable voltage and power down to stop receiving host commands.

AES 256
AES 256 (Advanced Encryption Standard with a 256-bit key) is a powerful encryption technology used to keep data secure and confidential. It works by encrypting data and allowing it to be decrypted when needed.

TCG OPAL
Self-Encrypting Drives (SEDs) integrate hardware-based encryption to secure data at rest. A Media Encryption Key (MEK) encrypts and decrypts data, protecting sensitive information in applications like IoT, industrial systems, and medical devices.

SP Toolbox
Understanding SSD Endurance
Two key metrics are used to estimate SSD endurance:
Total Bytes Written (TBW): Calculated using the formula:
TBW = Physical Capacity × NAND Program/Erase Cycles ÷ Write Amplification Factor ÷ Wear Leveling Factor.
Drive Writes Per Day (DWPD): Defined as:
Advanced Sorting Technology
SP Industrial implements Advanced Sorting Technology (AST) for NAND Flash testing and classification, specifically designed to meet the diverse temperature requirements of industrial customers.This technology precisely evaluates the durability and stability of NAND Flash memory; then accurately classifies it based on rigorous test results. This meticulous process ensures that the classified NAND Flash fully complies with the stringent demands of wide-temperature industrial applications.

Garbage Collection
Solid-state drives (SSDs) utilize NAND flash memory to store data, employing a process managed by the controller to ensure efficient storage and retrieval. Unlike traditional storage methods, SSDs cannot directly overwrite old data with new data. Instead, the existing data in the relevant block must first be erased before new data can be written. This process is facilitated through a mechanism known as Garbage Collection.

Bad Block Management
Bad Block Management is a mechanism used by the controller in flash memory to detect and handle bad blocks. It identifies and marks unusable blocks to ensure they are excluded from future data storage.

pSLC
SP Industrial bridges the gap between SLC and MLC/3D TLC solutions with pseudo-SLC (pSLC) Flash, a more advanced variant of MLC/3D TLC. pSLC offers faster speeds, higher program/erase cycle endurance, and better reliability than standard MLC/3D TLC, while being more cost-effective than SLC. It operates similarly to SLC but has fewer program/erase cycles, making it an efficient choice for applications demanding high endurance.

Wear Leveling
Wear leveling is a crucial technique for addressing the inherent limitations of NAND flash memory. It manages the wear rate across the entire NAND flash device, ensuring that each memory block is utilized as evenly as possible. Effective wear leveling is essential for maximizing the lifespan and reliability of the flash device.